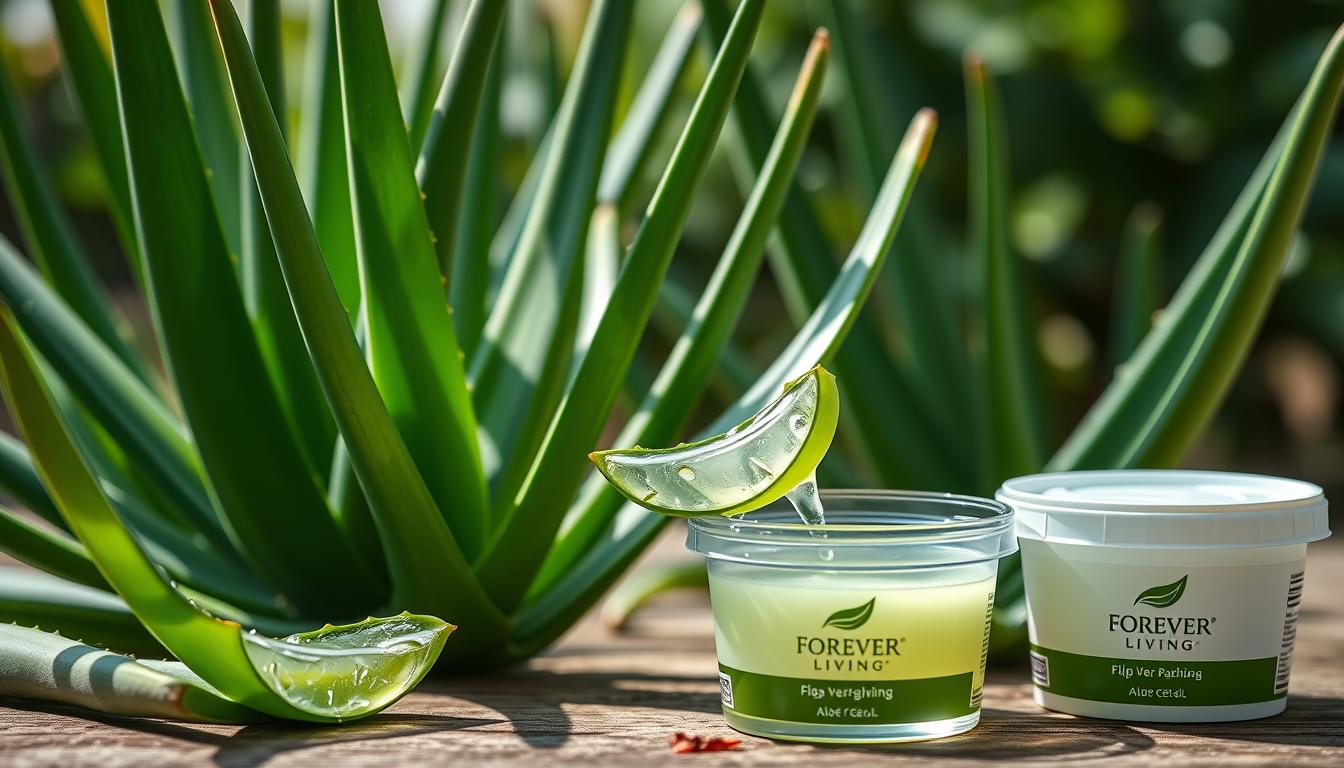
For centuries, aloe vera has been a cornerstone in traditional medicine for treating various skin conditions. This succulent plant, scientifically known as Aloe barbadensis miller, has earned its reputation as nature’s healer for inflammatory skin disorders like eczema and psoriasis. Today, modern dermatology is taking a renewed interest in aloe vera for eczema and psoriasis management, examining its therapeutic properties through the lens of scientific research.
Fresh aloe vera gel contains numerous bioactive compounds beneficial for inflammatory skin conditions
While conventional treatments remain the first line of defense against these challenging skin conditions, many dermatologists now recognize the complementary benefits that aloe vera may provide. This article explores dermatologist-approved ways to incorporate aloe vera into your skincare routine for managing eczema and psoriasis symptoms.
Benefits of Aloe Vera for Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Aloe vera’s therapeutic potential for skin conditions stems from its rich composition of bioactive compounds. The plant contains over 75 potentially active constituents, including vitamins, enzymes, minerals, sugars, lignin, saponins, salicylic acids, and amino acids.
Aloe vera contains complex polysaccharides and glycoproteins that contribute to its healing properties
Key compounds in aloe vera that benefit inflammatory skin disorders include:
- Polysaccharides: Large sugar molecules like acemannan that promote skin healing and reduce inflammation
- Glycoproteins: Compounds that help reduce pain and inflammation
- Anthraquinones: Natural compounds with antibacterial and antiviral properties
- Plant sterols: Substances that reduce inflammation similar to cortisone
Proven Benefits for Skin Health
Research has identified several ways aloe vera may help those suffering from eczema and psoriasis:
- Anti-inflammatory action: Aloe vera inhibits the inflammatory pathway, reducing redness, swelling, and discomfort associated with eczema and psoriasis flares
- Enhanced moisturization: The gel provides deep hydration, addressing the dry skin characteristic of both conditions
- Antimicrobial protection: Helps prevent secondary infections in cracked or broken skin common with eczema
- Wound healing acceleration: Stimulates fibroblast activity, promoting faster healing of skin lesions
- Immune modulation: May help regulate overactive immune responses in psoriasis
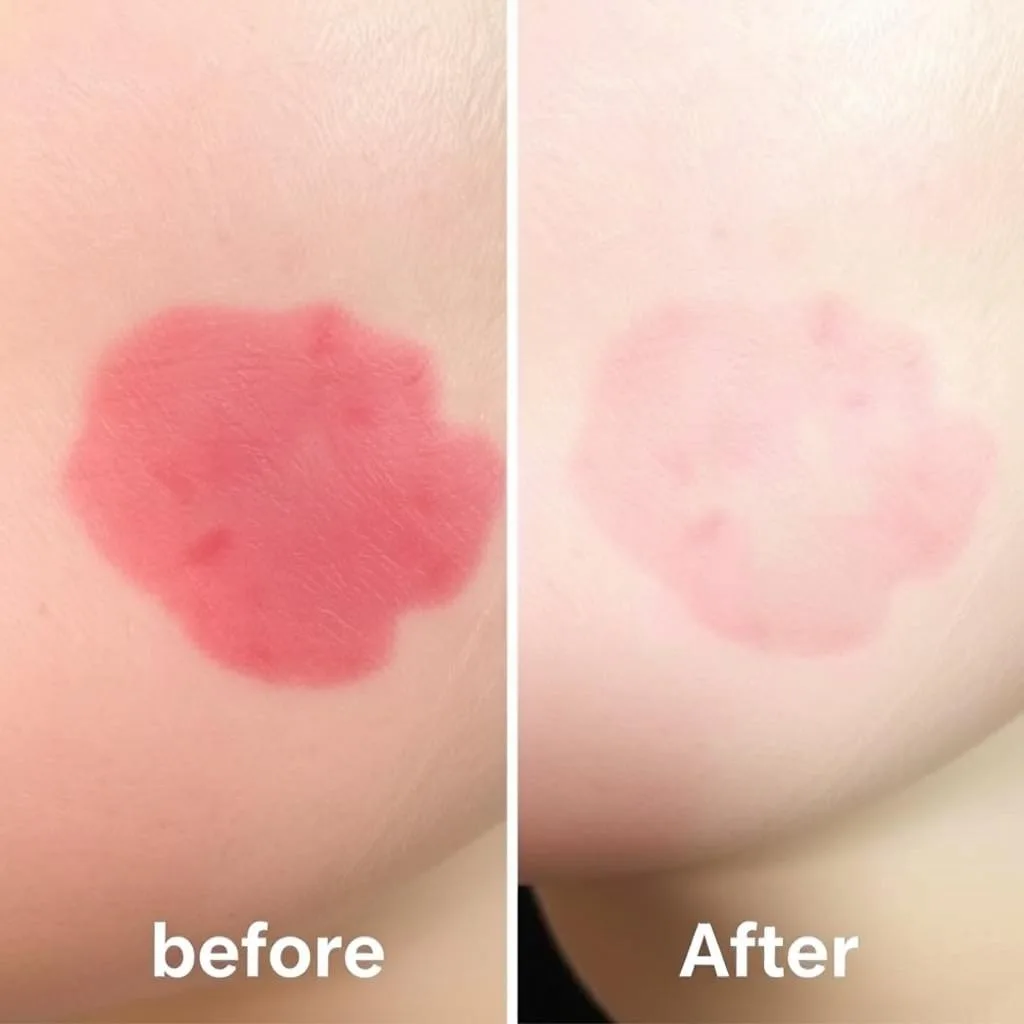

Find Relief for Your Skin Condition
Wondering if aloe vera could help your specific skin concerns? Our dermatology experts can provide personalized advice.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Aloe Vera for Eczema and Psoriasis
While anecdotal evidence for aloe vera’s benefits is abundant, scientific research provides more concrete support for its use in inflammatory skin disorders. Here’s what clinical studies reveal about aloe vera for eczema and psoriasis:

Dermatologists increasingly recognize aloe vera’s potential benefits for inflammatory skin conditions
Key Research Findings
- Psoriasis Study (2018): A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Dermatological Treatment found that a cream containing 0.5% aloe vera extract significantly reduced psoriasis symptoms compared to placebo. Participants showed a 72.5% improvement in Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) scores after 8 weeks of application.
- Eczema Research (2020): A clinical investigation in the International Journal of Dermatology demonstrated that aloe vera gel combined with standard moisturizers improved skin hydration by 88% and reduced itching by 67% in atopic dermatitis patients compared to moisturizer alone.
- Comparative Analysis (2022): A systematic review examining 12 studies concluded that topical aloe vera preparations showed efficacy comparable to 1% hydrocortisone for mild eczema, with fewer side effects. The review highlighted aloe’s potential as a complementary treatment alongside conventional therapies.
“The evidence suggests that aloe vera can be a valuable addition to treatment regimens for inflammatory skin conditions. While not a replacement for conventional therapies, it offers complementary benefits with minimal risk when used appropriately.”
— Dr. Sarah Jennings, Board-Certified Dermatologist
These studies support what many have experienced anecdotally: aloe vera may provide meaningful relief for both eczema and psoriasis when used consistently as part of a comprehensive skin care approach.
Dermatologist-Approved Routines Using Aloe Vera
Incorporating aloe vera into your skincare routine requires a systematic approach for maximum benefit. Dermatologists recommend the following routines for effectively using aloe vera for eczema and psoriasis management:

Choose high-quality aloe vera products with minimal additives for best results
Morning Routine for Eczema
- Gentle cleansing: Wash affected areas with lukewarm water and a fragrance-free, pH-balanced cleanser
- Pat dry: Gently pat skin with a soft towel, leaving it slightly damp
- Apply aloe vera: Spread a thin layer of pure aloe vera gel on affected areas
- Allow absorption: Wait 5-10 minutes for the gel to fully absorb
- Moisturize: Apply your regular eczema-friendly moisturizer over the aloe vera
- Sun protection: Finish with a mineral-based, fragrance-free sunscreen if going outdoors
Evening Routine for Psoriasis
- Gentle exfoliation: Once weekly, use a soft washcloth to gently remove scales (skip this step during flares)
- Cleanse: Use a gentle, soap-free cleanser
- Warm compress: Apply a warm (not hot) compress to affected areas for 5 minutes to enhance absorption
- Apply aloe vera: Apply a generous layer of aloe vera gel to psoriasis plaques
- Occlusion: For severe areas, consider covering with cotton gloves or clothing to enhance penetration overnight
- Consistency: Repeat nightly for at least 8 weeks to evaluate effectiveness
Apply aloe vera gel directly to psoriasis plaques using gentle, circular motions
Flare-Up Management Protocol
During active flares of either condition, increase application frequency to 3-4 times daily. Apply a thicker layer of aloe vera gel and consider refrigerating the gel for added anti-inflammatory benefits from the cooling effect.
Product Selection Tips
- Choose products with at least 95% aloe vera content
- Avoid formulations with alcohol, fragrances, or dyes
- Look for products in opaque containers to preserve potency
- Consider refrigerated aloe vera for enhanced soothing effects
- Fresh aloe leaf gel is ideal if available
Application Techniques
- Apply to slightly damp skin for better absorption
- Use gentle, circular motions to enhance penetration
- Layer thinner rather than thicker for daytime use
- Apply more generously for overnight treatment
- Consider mixing with a few drops of vitamin E oil for enhanced benefits
Get Personalized Skin Care Advice
Every skin condition is unique. Our dermatologists can help create a customized aloe vera treatment plan for your specific needs.
Safety and Precautions When Using Aloe Vera
While aloe vera is generally safe for topical use, certain precautions should be taken, especially for those with sensitive skin or severe inflammatory skin disorders.
Always perform a patch test before applying aloe vera to larger areas of affected skin
Patch Test Instructions
- Apply a small amount of aloe vera to a quarter-sized area on your inner forearm
- Cover with a bandage and leave for 24 hours
- Remove the bandage and check for any signs of irritation, redness, or allergic reaction
- If no reaction occurs, it’s likely safe to use on larger areas
- If irritation develops, discontinue use and consult a dermatologist
Important: Aloe vera should not replace prescribed medications for severe eczema or psoriasis. Always consult with a dermatologist before making changes to your treatment regimen.
When to Avoid Aloe Vera
- Known allergy to plants in the Liliaceae family (including garlic, onions, and tulips)
- Open wounds or infected skin areas
- Very severe or unstable psoriasis or eczema
- During treatment with phototherapy (unless approved by your dermatologist)
- If using certain topical medications that may interact with aloe vera

Consult with a dermatologist before starting any new treatment for chronic skin conditions
Potential Side Effects
Though rare, some individuals may experience:
- Mild burning or stinging sensation
- Contact dermatitis (skin rash)
- Increased dryness in some cases
- Photosensitivity (increased sensitivity to sunlight)
If you experience any of these side effects, discontinue use and consult with a healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions About Aloe Vera for Skin Conditions
Can aloe vera completely cure eczema or psoriasis?
No, aloe vera cannot cure eczema or psoriasis, as these are chronic conditions without permanent cures. However, aloe vera may help manage symptoms and reduce flare-up severity when used as part of a comprehensive treatment approach. It works best as a complementary therapy alongside conventional treatments recommended by your dermatologist.
How often should I apply aloe vera to affected areas?
For maintenance, applying aloe vera 2-3 times daily is typically recommended. During flare-ups, you may increase to 3-4 applications daily. Consistency is key—regular application over several weeks provides better results than occasional use. Always follow your dermatologist’s specific recommendations for your condition.
Is fresh aloe vera better than commercial products?
Fresh aloe vera gel extracted directly from the plant contains the highest concentration of active compounds. However, high-quality commercial products with at least 95% aloe vera content can be equally effective and more convenient. If using commercial products, look for those without added fragrances, alcohol, or preservatives that might irritate sensitive skin.

Fresh aloe vera gel can be extracted directly from the plant for maximum potency
Can children use aloe vera for eczema?
Aloe vera is generally considered safe for children with eczema, but always consult with a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist first. Use only pure aloe vera products without additives, and always perform a patch test. For very young children under 2 years, medical guidance is especially important before trying any new topical treatment.
Can aloe vera interact with other skin medications?
Yes, aloe vera may potentially interact with certain topical medications. It can enhance the absorption of some creams and ointments, which might be beneficial in some cases but problematic in others. Always inform your dermatologist about all products you’re using, and consider waiting 30-60 minutes between applying prescription medications and aloe vera unless otherwise directed.
Conclusion
Consistent use of aloe vera as part of a comprehensive treatment plan may help improve skin condition over time
Aloe vera for eczema and psoriasis represents a promising complementary approach to managing these challenging inflammatory skin disorders. Its natural anti-inflammatory, moisturizing, and antimicrobial properties make it a valuable addition to many skincare routines. While not a replacement for medical treatment, when used consistently and correctly, aloe vera may help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life for those suffering from these conditions.
Remember that individual responses to aloe vera vary, and what works for one person may not work for another. The key is to approach treatment methodically, perform proper patch testing, and maintain open communication with your dermatologist about all aspects of your skincare regimen.
If you’re considering incorporating aloe vera into your eczema or psoriasis management plan, consult with a dermatologist who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific condition, severity, and overall health profile.
Take the Next Step in Managing Your Skin Condition
Ready to explore how aloe vera for eczema and psoriasis might benefit your skin? An experienced dermatologists can help determine if it’s right for you.







