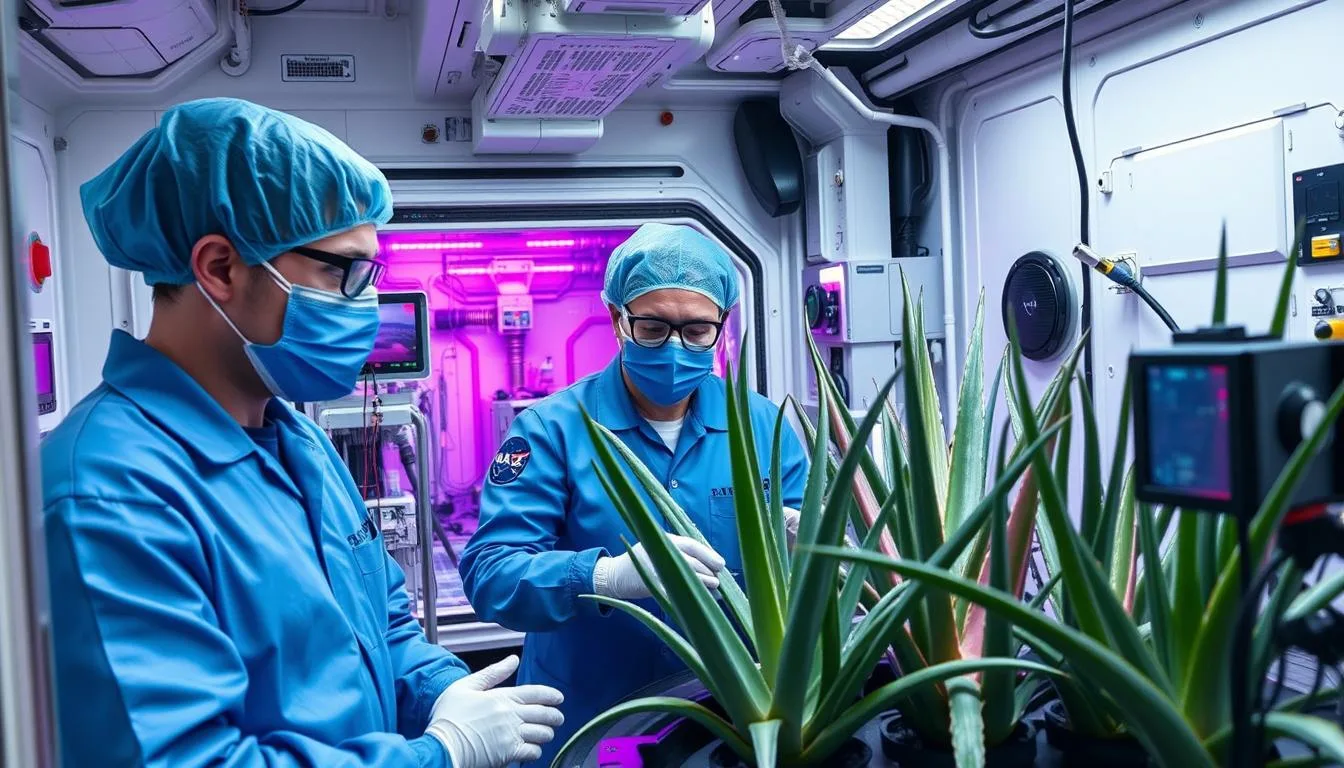
As humanity ventures further into space, the challenge of creating sustainable life support systems becomes increasingly crucial. Among the many plants being studied for space agriculture, Aloe Vera stands out for its remarkable versatility. This resilient succulent not only offers medicinal properties for astronaut healthcare but also contributes to air purification and potential radiation protection. NASA’s ongoing experiments with Aloe Vera cultivation in microgravity environments are paving the way for its integration into future Mars and Moon colonies, where every resource must serve multiple purposes.
- NASA's Experiments with Aloe Vera in Space
- The Dual Role of Aloe Vera for Space Missions
- Challenges of Zero-Gravity Farming
- Learn More Bout NASA's Plant Research
- Aloe Vera in Future Mars and Moon Colonies
- Technical Adaptations for Space Cultivation
- Harvesting and Processing in Space
- Implications for Earth-Based Agriculture
- Future Research Directions
- Conclusion: The Future of Aloe Vera in Space
- Download Research Guide
- NASA's Experiments with Aloe Vera in Space
- The Dual Role of Aloe Vera for Space Missions
- Challenges of Zero-Gravity Farming
- Learn More Bout NASA's Plant Research
- Aloe Vera in Future Mars and Moon Colonies
- Technical Adaptations for Space Cultivation
- Harvesting and Processing in Space
- Implications for Earth-Based Agriculture
- Future Research Directions
- Conclusion: The Future of Aloe Vera in Space
- Download Research Guide
NASA's Experiments with Aloe Vera in Space
NASA scientists monitoring Aloe Vera growth in the Advanced Plant Habitat aboard the ISS
NASA has been conducting extensive research on plant growth in space environments through programs like Veggie and the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH). While initial experiments focused on fast-growing leafy greens and flowering plants, researchers have expanded their studies to include more specialized plants like Aloe Vera, which offers unique benefits for long-duration missions.
Hydroponic Systems for Zero-Gravity Cultivation
Traditional soil-based growing methods face significant challenges in microgravity, where water forms bubbles rather than flowing downward. To address this, NASA scientists have adapted hydroponic systems specifically for Aloe Vera cultivation in space. These systems use a carefully calibrated nutrient solution delivered directly to the plant roots through specialized “pillows” filled with clay-based growth media and controlled-release fertilizer.
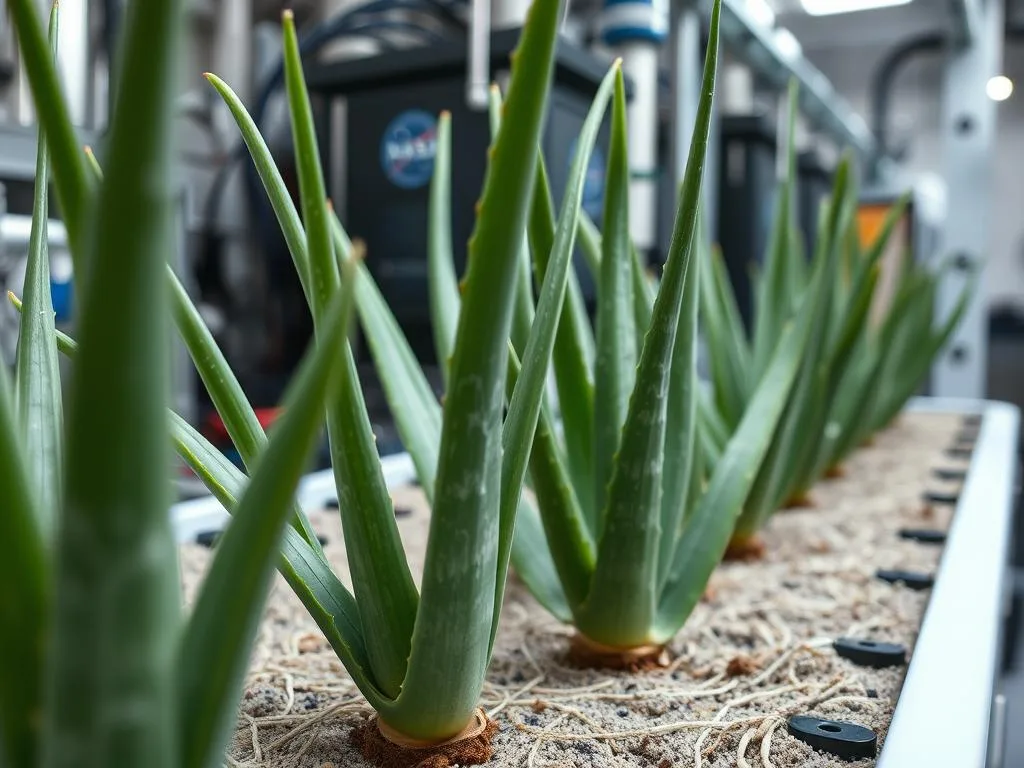

Specialized hydroponic system designed for Aloe Vera cultivation in microgravity
LED Lighting Adaptations
In the absence of natural sunlight, NASA has developed specialized LED lighting systems that provide the optimal spectrum for Aloe Vera growth. Unlike the typical red-blue combination used for leafy greens, Aloe Vera benefits from a modified spectrum that includes additional far-red wavelengths. The Advanced Plant Habitat provides this customized lighting along with automated monitoring through more than 180 sensors that track growth parameters.
According to NASA research, “In the absence of gravity, plants use other environmental factors, such as light, to orient and guide growth.” This principle has been essential in developing effective cultivation methods for Aloe Vera in space, where the plant must rely on light cues rather than gravitational signals to determine growth direction.
The Dual Role of Aloe Vera for Space Missions
Astronaut Skincare and Health Applications
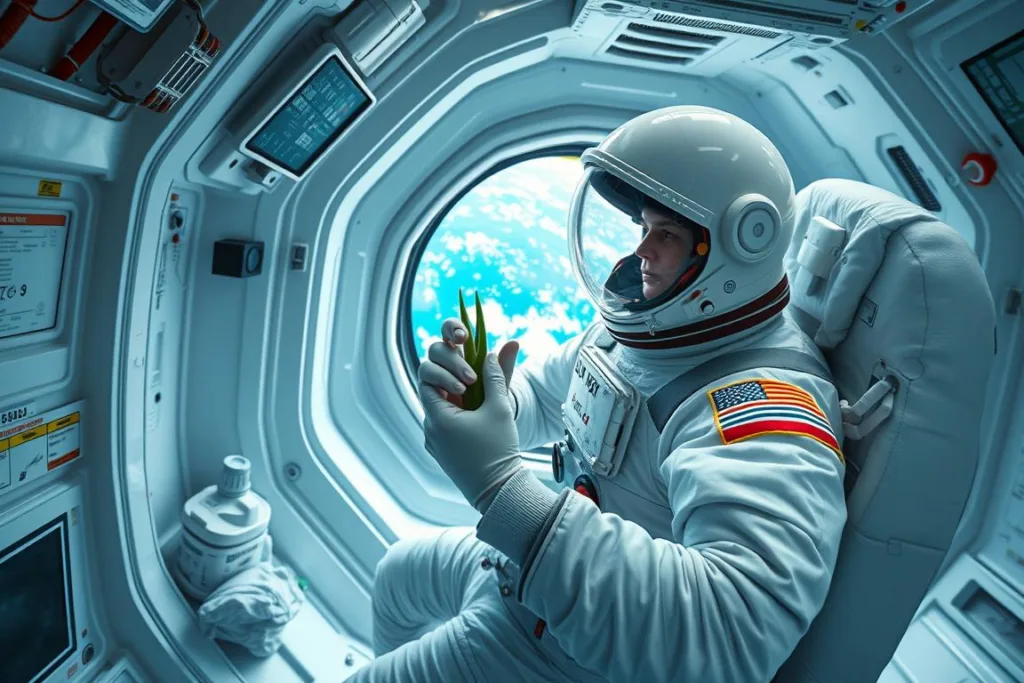

Astronaut utilizing fresh Aloe Vera gel for skincare in space
Space environments present unique challenges for human skin health. Microgravity, radiation exposure, and the artificial atmosphere of spacecraft can lead to skin dryness, irritation, and delayed wound healing. Aloe Vera’s well-documented healing properties make it an ideal natural remedy for these conditions.
The plant’s gel contains compounds that provide radiation protection by scavenging free radicals generated by cosmic radiation exposure. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties support wound healing in the challenging space environment, where the human immune system is often compromised.
Environmental Sustainability Functions
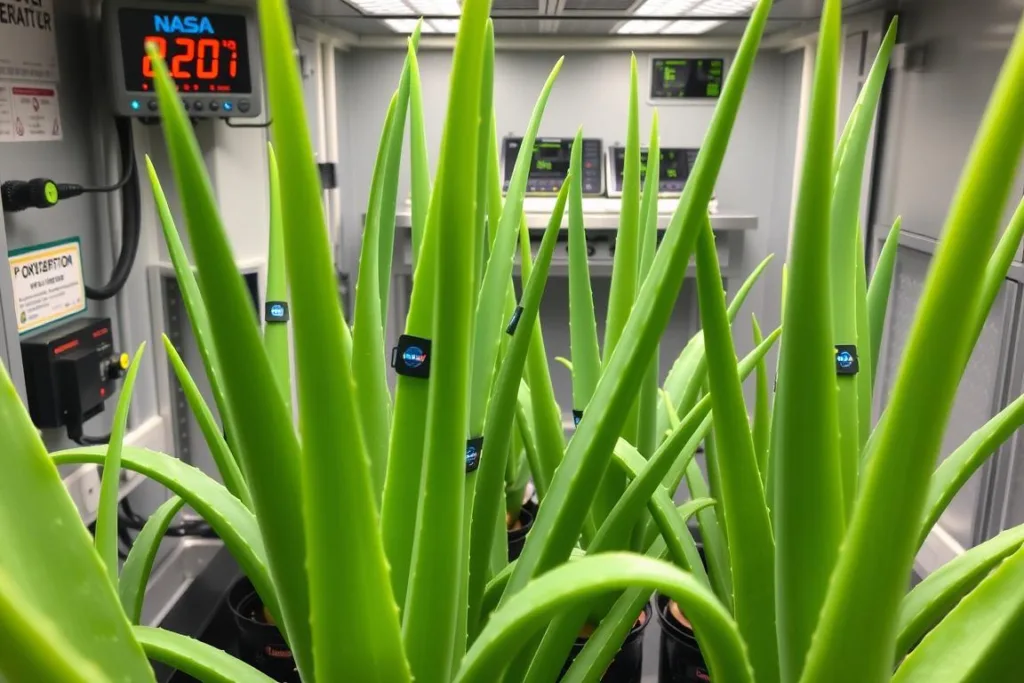

Aloe Vera plants being monitored for oxygen production and CO2 absorption
Beyond its medicinal applications, Aloe Vera serves crucial environmental functions in space habitats. Like other plants, it absorbs carbon dioxide and releases oxygen through photosynthesis, contributing to air revitalization systems. What makes Aloe Vera particularly valuable is its high efficiency in this process despite relatively low water requirements.
NASA research has shown that Aloe Vera is effective at removing specific airborne pollutants, including formaldehyde and benzene, which can accumulate in the closed environment of spacecraft. This natural air purification capability adds another dimension to its utility in space agriculture systems.
Challenges of Zero-Gravity Farming
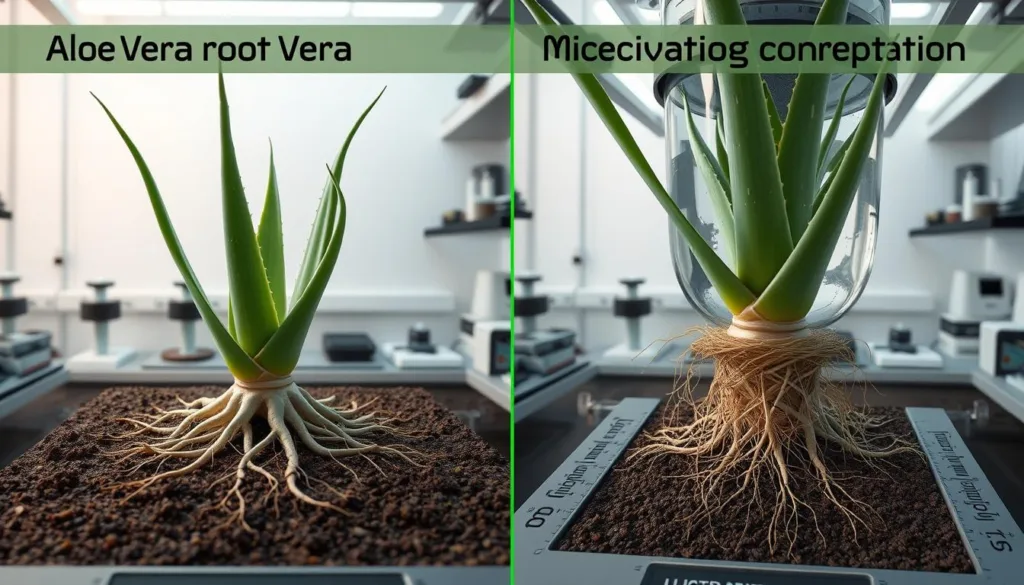

Comparison of Aloe Vera root development in Earth gravity versus microgravity
Root Behavior in Microgravity
One of the most significant challenges in cultivating Aloe Vera in space is the altered behavior of plant roots in microgravity. On Earth, roots naturally grow downward in response to gravity (gravitropism). In space, this directional cue is absent, leading to disoriented root growth patterns that can affect nutrient uptake and plant stability.
NASA scientists have observed that Aloe Vera roots in microgravity tend to grow in random directions, sometimes curling back toward the plant or growing horizontally. To address this challenge, researchers have developed specialized growth chambers with subtle directional cues to guide root development.
Water Distribution Solutions
Specialized watering system designed for even moisture distribution in microgravity
Water management presents another significant challenge in space agriculture. As NASA researchers note, “In the absence of gravity, plants use other environmental factors, such as light, to orient and guide growth. Since plants reflect a lot of green light and use more red and blue wavelengths, the Veggie chamber typically glows magenta pink.”
For Aloe Vera specifically, NASA has developed specialized watering systems that use capillary action and carefully designed porous materials to ensure even moisture distribution around the roots. These systems prevent both drowning and dehydration by maintaining optimal moisture levels despite the absence of gravity-driven water flow.
Access NASA's Plant Research Resources
Explore NASA’s comprehensive guides and research papers on space plant cultivation techniques and technologies.
Aloe Vera in Future Mars and Moon Colonies
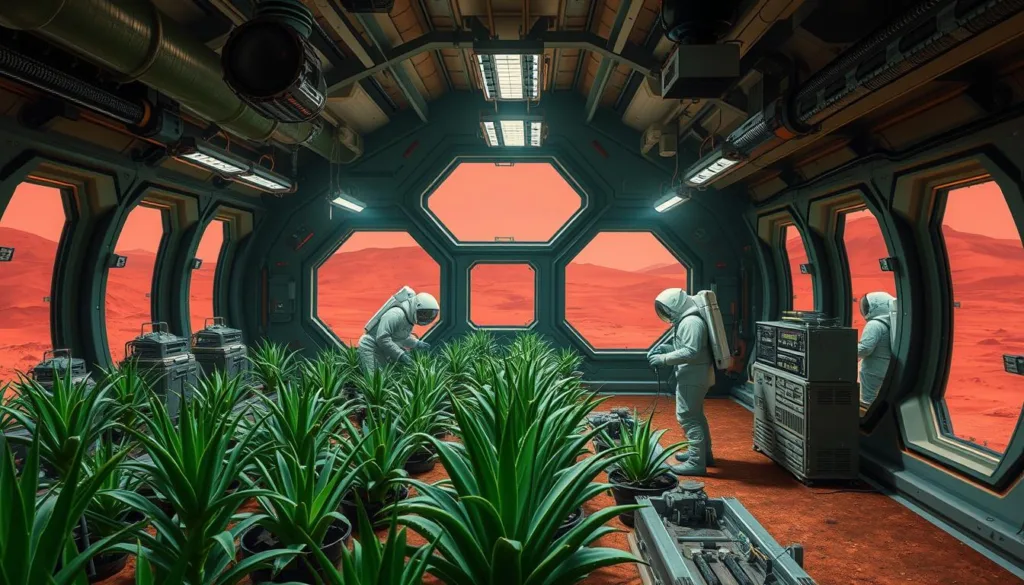

Conceptual rendering of an Aloe Vera cultivation section in a Mars habitat
Closed-Loop Life Support Systems
Future space colonies on Mars or the Moon will require self-sustaining, closed-loop life support systems where resources are continuously recycled. Aloe Vera’s multiple functions make it an ideal component of such systems. Its ability to thrive in relatively harsh conditions with minimal water aligns perfectly with the resource constraints of extraterrestrial habitats.
In these closed systems, Aloe Vera would serve multiple roles: producing oxygen, absorbing carbon dioxide, purifying air by removing volatile organic compounds, providing medicinal resources, and potentially contributing to food production through its nutritional components.
Radiation Protection Applications
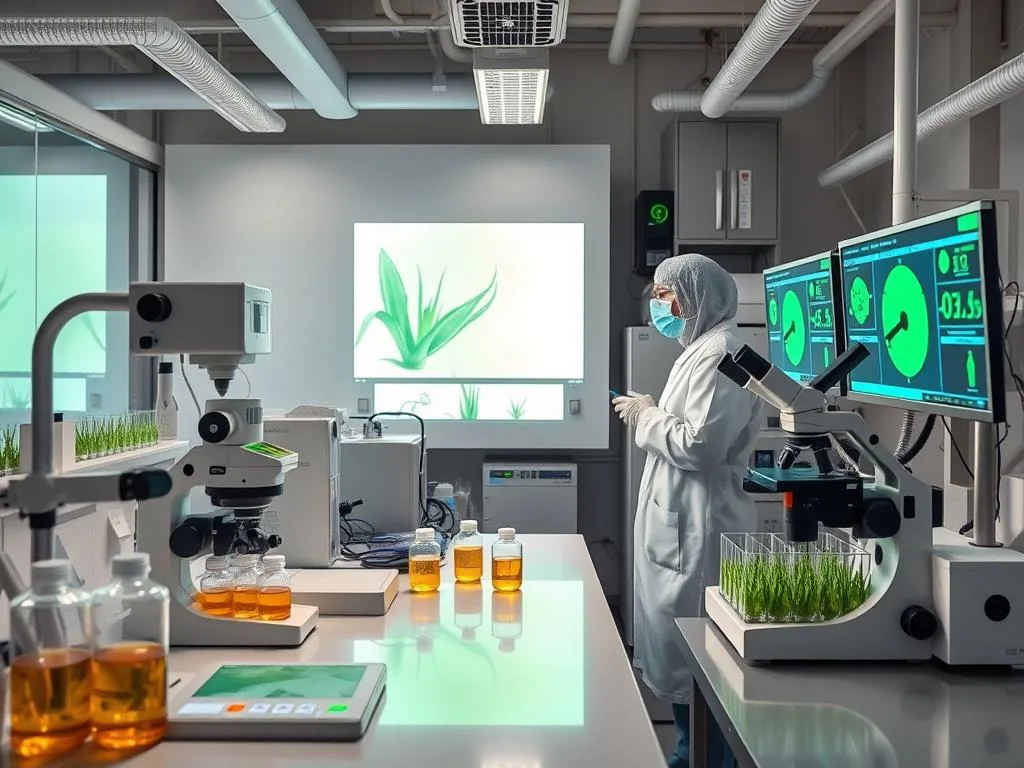

Laboratory testing of Aloe Vera extracts for radiation protection properties
The radiation environment on Mars and the Moon presents significant challenges for human habitation. Aloe Vera’s natural compounds have shown promise in providing some radiation protection, both when applied topically and when consumed. NASA researchers are investigating how concentrated Aloe Vera extracts might be incorporated into habitat materials or astronaut protective equipment.
Dr. Norman Lewis, a principal investigator for NASA plant studies, notes that “This fundamental science information will guide our strategies for deep space exploration and colonization.” The radiation-protective properties of Aloe Vera could prove essential for long-term human presence beyond Earth’s protective magnetosphere.
Technical Adaptations for Space Cultivation
Genetic Modifications for Space Resilience
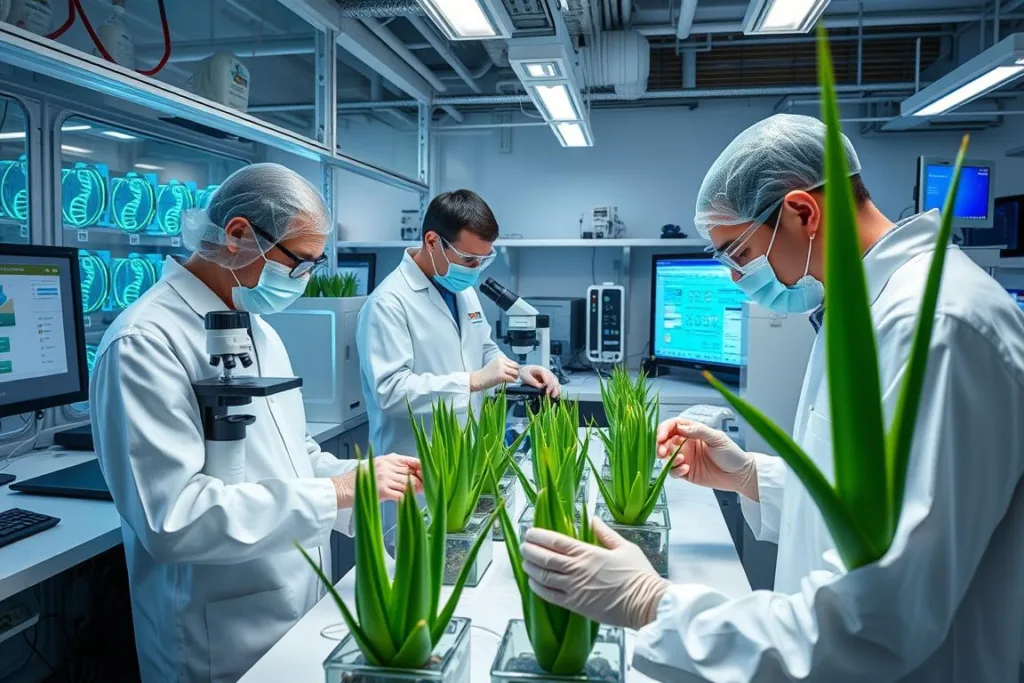

Research on genetic modifications to enhance Aloe Vera’s space resilience
NASA scientists are exploring genetic modifications that could enhance Aloe Vera’s suitability for space environments. One promising area of research involves reducing the plant’s lignin content. As NASA research indicates, “Lewis and his team also want to know if plants genetically engineered to have less lignin can survive and function normally in space.”
Reduced lignin content could make Aloe Vera more efficient in terms of nutrient absorption and waste processing, while potentially maintaining its structural integrity in microgravity. This adaptation would make the plant even more valuable in closed-loop life support systems.
Automated Cultivation Systems
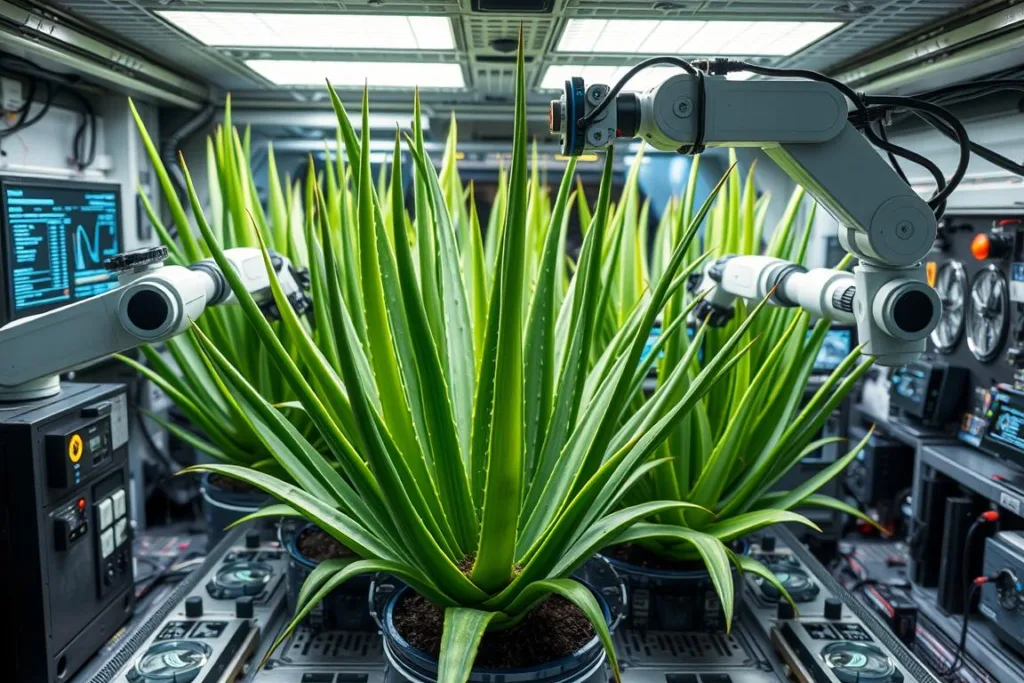

Automated system for monitoring and maintaining Aloe Vera in space
To minimize crew time requirements, NASA is developing automated systems for Aloe Vera cultivation in space. Similar to the Advanced Plant Habitat, these systems would monitor plant health, adjust environmental conditions, and even harvest mature leaves when needed, all with minimal human intervention.
These automated systems use machine learning algorithms to optimize growing conditions based on continuous data collection from multiple sensors. As NASA explains, the Advanced Plant Habitat “is enclosed and automated with cameras and more than 180 sensors that are in constant interactive contact with a team on the ground.”
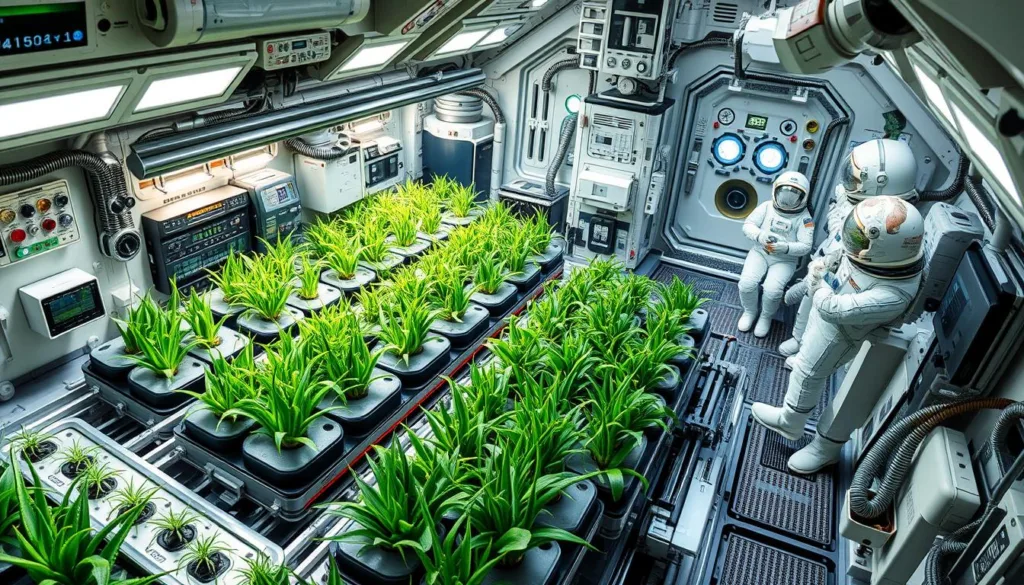

Integrated space agriculture system featuring Aloe Vera alongside other crops
Harvesting and Processing in Space
Specialized Harvesting Techniques
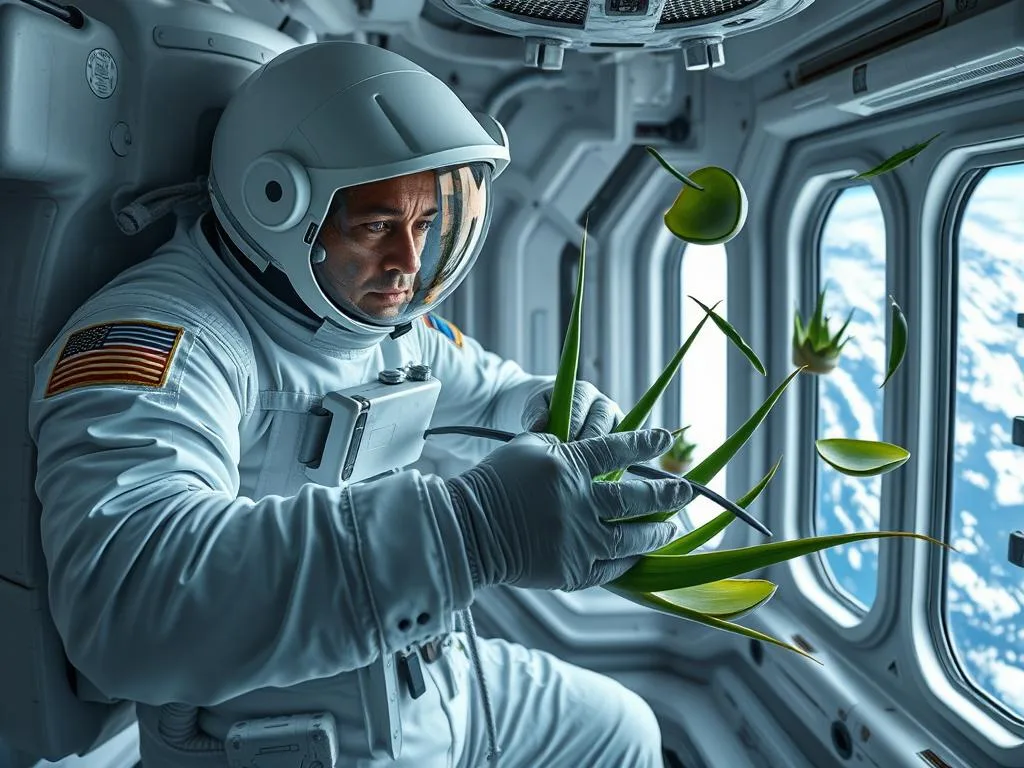

Specialized techniques for harvesting Aloe Vera in microgravity
Harvesting Aloe Vera in space presents unique challenges due to the plant’s gel-filled leaves and the microgravity environment. NASA has developed specialized cutting tools and containment systems to prevent gel dispersion during harvesting, which could otherwise damage sensitive equipment or create air quality issues.
The harvesting process is carefully timed to maximize the medicinal properties of the gel while ensuring the plant’s continued growth. As with Earth-based cultivation, only the mature outer leaves are harvested, allowing the plant to continue producing new growth from its center.
Gel Extraction and Preservation
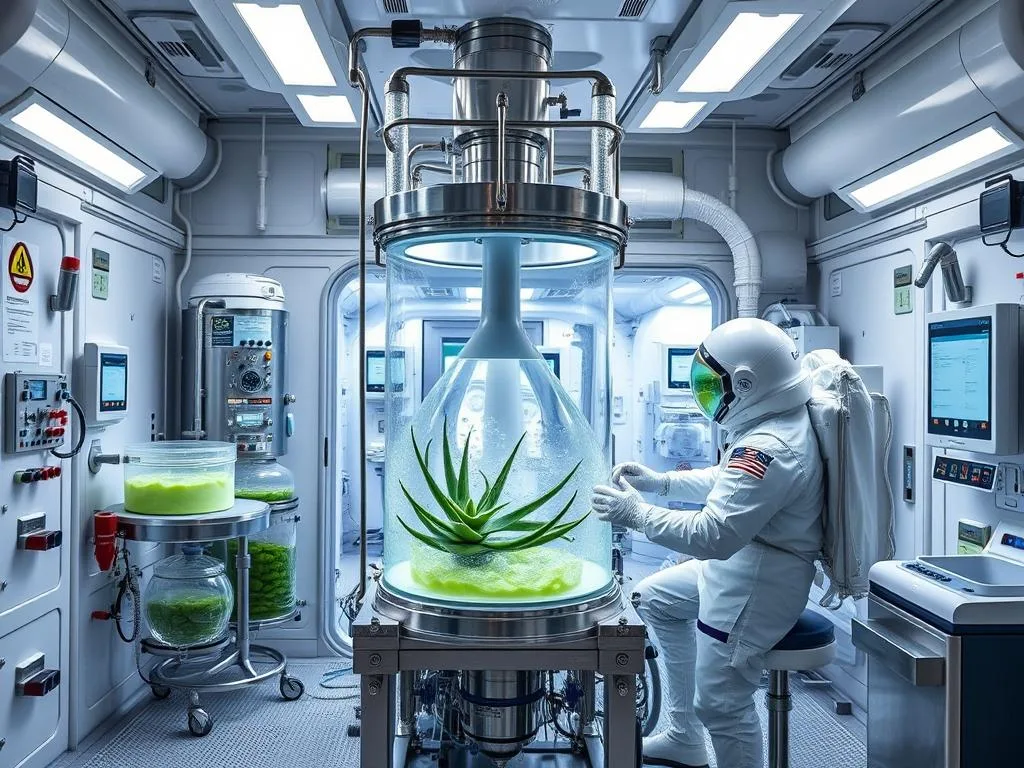

Specialized equipment for extracting and preserving Aloe Vera gel in space
Once harvested, the Aloe Vera leaves undergo a specialized extraction process to collect and preserve the valuable inner gel. NASA has adapted Earth-based techniques for the space environment, creating sealed processing units that prevent contamination while efficiently separating the gel from the outer leaf material.
The extracted gel is then stabilized using preservation methods compatible with space environments. These methods avoid traditional preservatives that might introduce unnecessary chemicals into the closed life support system, instead relying on physical preservation techniques like controlled dehydration or cold storage.
Implications for Earth-Based Agriculture
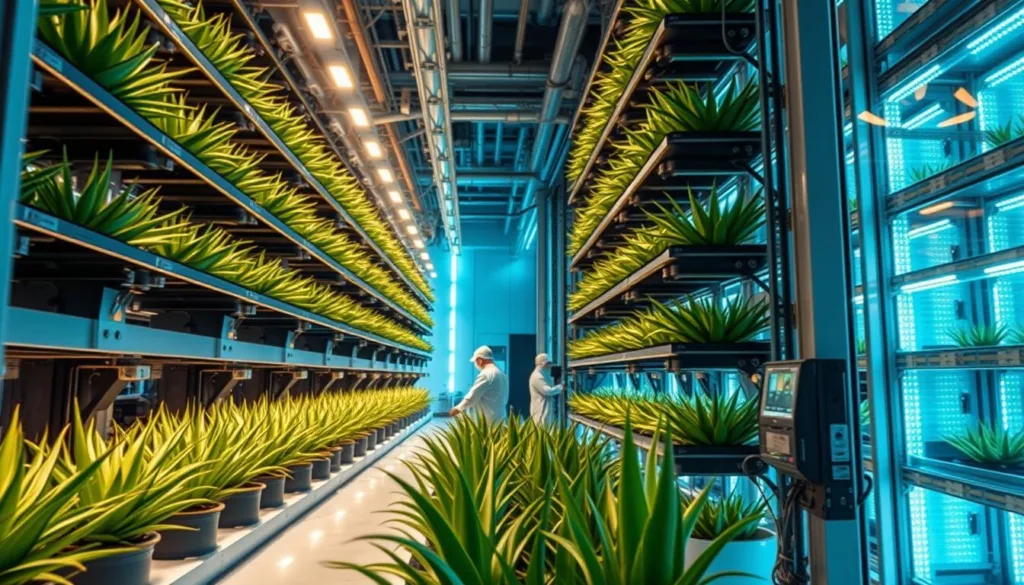

Vertical farming system utilizing space-derived technologies for efficient Aloe Vera cultivation
The technologies and techniques developed for space cultivation of Aloe Vera have significant implications for Earth-based agriculture, particularly in resource-constrained environments. The water-efficient hydroponic systems designed for space can be adapted for arid regions facing water scarcity, while the optimized LED lighting systems can improve indoor and vertical farming operations.
NASA’s research on plant responses to stress in space environments is also yielding insights into improving plant resilience on Earth. As climate change creates more challenging growing conditions in many regions, the adaptations developed for space agriculture could help terrestrial farmers maintain productivity with fewer resources.
Benefits of Space-Derived Aloe Vera Cultivation
- Enhanced water efficiency through precision irrigation systems
- Optimized lighting spectra for maximum photosynthetic efficiency
- Improved understanding of plant stress responses and adaptations
- Development of automated monitoring and maintenance systems
- Advanced techniques for maximizing medicinal compound production
Challenges for Implementation
- High initial technology costs for specialized equipment
- Need for technical expertise to operate advanced systems
- Energy requirements for artificial lighting in indoor settings
- Adaptation of space-optimized systems to Earth’s gravity
- Scaling production to commercially viable levels
Future Research Directions

Scientists discussing future research directions for Aloe Vera in space agriculture
NASA’s ongoing research into Aloe Vera and other plants for space agriculture continues to evolve as new challenges and opportunities are identified. Future research directions include investigating the long-term genetic stability of plants grown through multiple generations in space, developing more sophisticated automated cultivation systems, and exploring the potential for using Aloe Vera in 3D bioprinting applications for habitat construction.
Another promising area is the investigation of symbiotic relationships between Aloe Vera and beneficial microorganisms that might enhance its growth and medicinal properties in space environments. These complex biological interactions could further improve the efficiency and sustainability of space agriculture systems.
Stay Updated on Space Agriculture Research
Join our newsletter to receive the latest updates on NASA’s space agriculture experiments, including Aloe Vera cultivation in microgravity and applications for future space colonies.
Conclusion: The Future of Aloe Vera in Space

Futuristic vision of Aloe Vera cultivation in an established Mars colony
As humanity extends its presence beyond Earth, the cultivation of versatile plants like Aloe Vera will play an increasingly important role in creating sustainable habitats. The dual functionality of Aloe Vera—providing both health benefits and environmental services—makes it particularly valuable for space agriculture systems where every resource must serve multiple purposes.
NASA’s ongoing experiments with Aloe Vera in microgravity environments are laying the groundwork for its integration into future Mars and Moon colonies. The challenges of cultivating this remarkable plant in space are substantial, but the potential benefits for astronaut health and habitat sustainability make it a worthwhile endeavor. As we continue to develop and refine these cultivation techniques, we move one step closer to establishing a permanent human presence beyond our home planet.
Explore More About Space Agriculture
Download our comprehensive guide to NASA’s plant experiments in space and learn how these innovations are shaping the future of both space exploration and sustainable agriculture on Earth.







